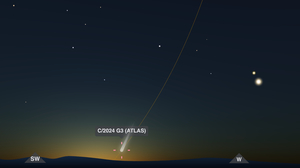
Best Comet of 2025?
C/2024 G3 (ATLAS) has already become very faintly visible to the naked eye for observers in the Southern Hemisphere.
Jewish communities in the UK mark Purim to remember the Jewish people’s deliverance from a royal death decree around the 4th century BCE, as told in the Book of Esther.

Graggers are noisemakers used during Purim.
©bigstockphoto.com/motimeiri
Purim is celebrated on the 14th day of Adar, the twelfth month of the Jewish calendar. The date falls in February or March in the Gregorian calendar. If the 14th of Adar falls on Sabbath, Purim celebrations are usually moved to a different date.
Purim is not a public holiday in the United Kingdom. It is not subject to business or work restrictions, unlike some other Jewish holidays. However, some Jewish authorities consider it disrespectful for Jewish people to treat Purim as a normal working day.
In synagogues all around the UK, Jewish communities gather to listen to a recitation of the Book of Esther, also known as the Megilla (or Megillah). Synagogues are often crowded during Purim. Some attendants, especially children, may be dressed in colorful costumes or wearing masks representing the characters found in the Megilla.
Whenever Haman, the villain of the story, is mentioned, the congregation may hiss, boo, or stamp their feet to drown out his name. Special Purim noisemakers, called graggers, are also used for this purpose.
Purim gift baskets called mishloach manot may be exchanged on this occasion. They usually include any type of food or drinks that are ready to be eaten and does not need any further preparation before consumption. According to tradition, the mishloach manot are meant to ensure that everyone has enough food and drink for the Purim feast.
Many Jewish people also donate to charity around this time of the year.
Purim is a joyous occasion commemorating the Jewish people’s deliverance from a royal death decree around the fourth century BCE, as told in the Book of Esther.
The United Kingdom is estimated to have the 5th largest Jewish population in the world, with just under 300,000 people practicing the Jewish faith in the country.
By far the largest British Jewish community is found in London, followed by those in Manchester and Leeds.
Jewish settlement in England can be traced as far back as the time of the Norman Conquest in 1066. The Jewish community outnumbered the Spanish and Portuguese communities in England by the 18th century.
Many Jewish families in Eastern Europe moved to England to escape persecution and hardship between 1881 and 1914. About 150,000 Jewish people settled in England, with large numbers staying at London's East End during that time. England continued to receive Jewish immigrants escaping persecution around the time of World War II (1939-1945).
In the Jewish diaspora—Jewish communities outside of Israel—an extra day is usually added to religious observances, with the exception of Yom Kippur, which lasts only one day worldwide, and Rosh Hashana, which is celebrated over two days in both Israel and the diaspora.
This custom has its roots in ancient times when the beginning of the months in the Jewish calendar still relied on the sighting of the crescent Moon following a New Moon.
The beginning of a new month was determined by the Sanhedrin, the supreme court of ancient Israel in Jerusalem. Once the date was published, messengers were dispatched to spread the news among Jews living abroad. Since this process took some time, it was decreed that Jews outside of ancient Israel were to observe every holiday for 2 days to make sure that the rules and customs applicable to each holiday were observed on the proper date. This rule is still observed today.
Note: Jewish holidays begin at sundown the day before the date specified for the holiday.
| Year | Weekday | Date | Name | Holiday Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 火曜日 | 3月10日 (火) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
| 2021 | 金曜日 | 2月26日 (金) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
| 2022 | 木曜日 | 3月17日 (木) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
| 2023 | 火曜日 | 3月7日 (火) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
| 2024 | 日曜日 | 3月24日 (日) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
| 2025 | 金曜日 | 3月14日 (金) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
| 2026 | 火曜日 | 3月3日 (火) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
| 2027 | 火曜日 | 3月23日 (火) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
| 2028 | 日曜日 | 3月12日 (日) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
| 2029 | 木曜日 | 3月1日 (木) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
| 2030 | 火曜日 | 3月19日 (火) | Purim | Jewish Holiday |
While we diligently research and update our holiday dates, some of the information in the table above may be preliminary. If you find an error, please let us know.

C/2024 G3 (ATLAS) has already become very faintly visible to the naked eye for observers in the Southern Hemisphere.

Orthodox Christians in the United Kingdom mark the start of a new calendar year on either January 1 or 14 in the Gregorian calendar.

Burns Night celebrates the life and work of Robert Burns and Scottish culture in general. It is on or around January 25 each year.

Isra and Mi'raj marks the night when the Prophet Mohammad traveled from Mecca to Jerusalem, ascended to heaven, and returned.