The Third Quarter Moon is a Half Moon
The Third Quarter Moon is when the opposite half of the Moon is illuminated compared to the First Quarter. Whether the lit up half appears on the left or right depends on where you are on Earth.

The Third Quarter Moon is the last of the four primary Moon phases.
©iStockphoto.com/Lio22
Jan 2025: See the planets at their best
The Crescent Moon, Saturn & Venus align in January 2025
C/2024 G3 (ATLAS): Best comet of 2025?
Next Third Quarter Moon
2025年1月22日 (水)5時30分
Previous Third Quarter Moon
2024年12月23日 (月)7時18分
Times for the Third Quarter Moon vary by time zone. Times and dates are based on the local time in Tokyo. Change location
Half the Moon Is Lit Up
The Third or Last Quarter Moon is also called a Half Moon because the Sun’s rays illuminate approximately 50% of the Moon’s surface seen from Earth.
Half of the Moon’s surface is always illuminated by direct sunlight, except during lunar eclipses when Earth casts its shadow on the Moon. Just how much of that light we can see from Earth varies every day, and we call this a Moon phase.
The Moon: Our natural satellite
Half Moon Visible During the Day
The Moon is the only astronomical object you can easily see in the day blue sky apart from the Sun. The Third Quarter Moon rises in the middle of the night and sets in the middle of the day. This is the opposite of a First Quarter Moon, which rises around midday and sets around midnight.
Last Primary Moon Phase
In western culture, we divide the lunar month into four primary and four intermediate Moon phases.
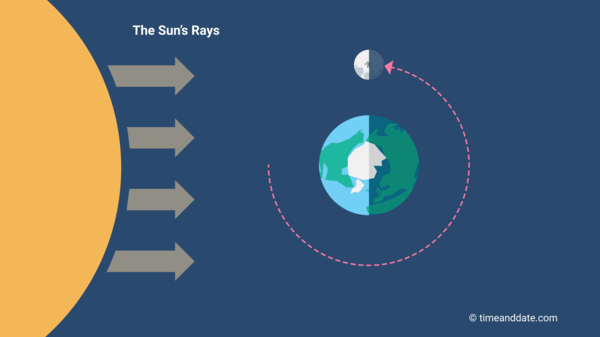
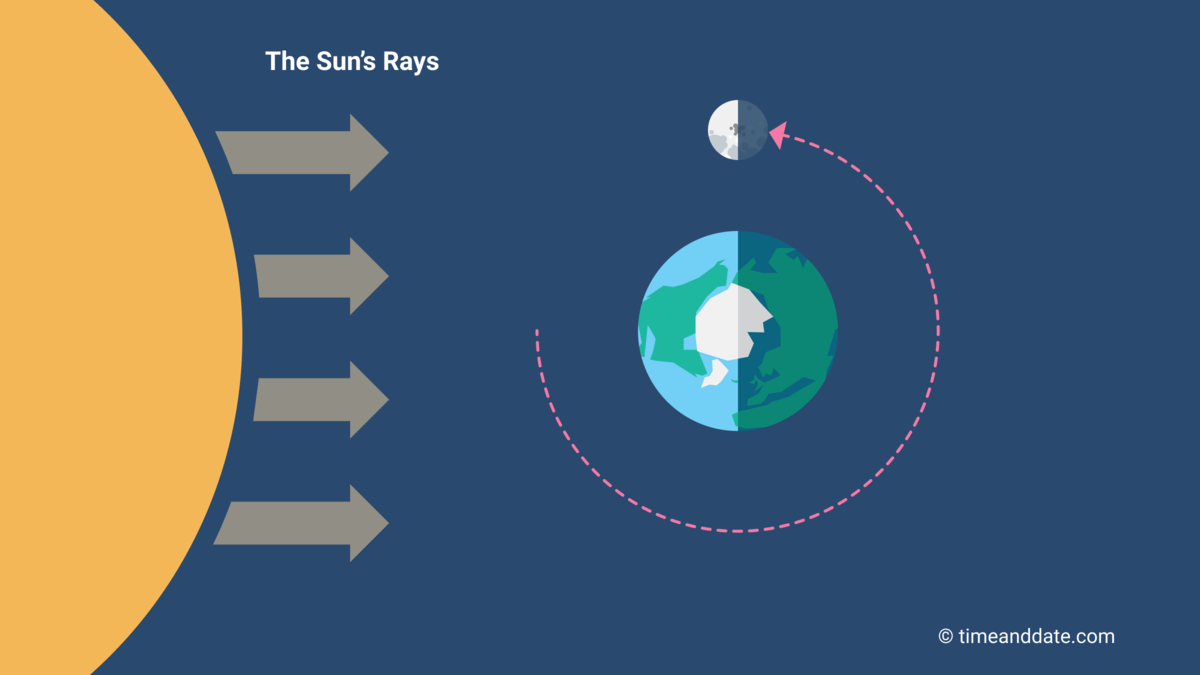
The Moon’s position at Third Quarter Moon.
©timeanddate.com
Third Quarter Moon is the last primary phase when the Moon has reached the third, or last, quarter of its orbit around Earth, hence the name.
A Primary Phase Is an Exact Time
The first primary Moon phase is New Moon, while the second is First Quarter Moon, and the third is called Full Moon.
The primary Moon phases occur at a specific moment in time, and the intermediate Moon phases are the time between the primary phases. These are the Waxing Crescent Moon, the Waxing Gibbous Moon, the Waning Gibbous Moon, and the Waning Crescent Moon.
Looks Different Around the Globe
Even though the Moon phases are the same all over the world, the Moon can look different in the sky. The same percentage and area of the Moon are lit up, but the Moon is rotated in different ways depending on the time, the date, your location, and the Moon’s position in the sky. Therefore, the illuminated part can appear on the left, the right, the top, or the bottom.
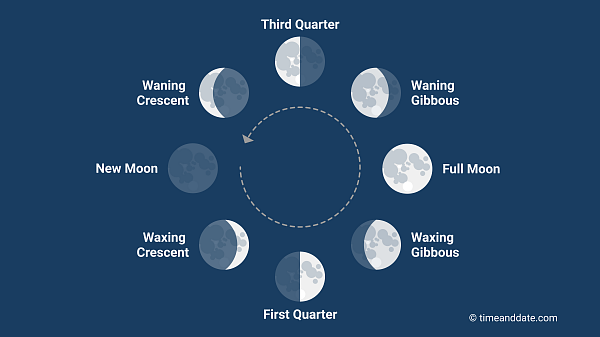
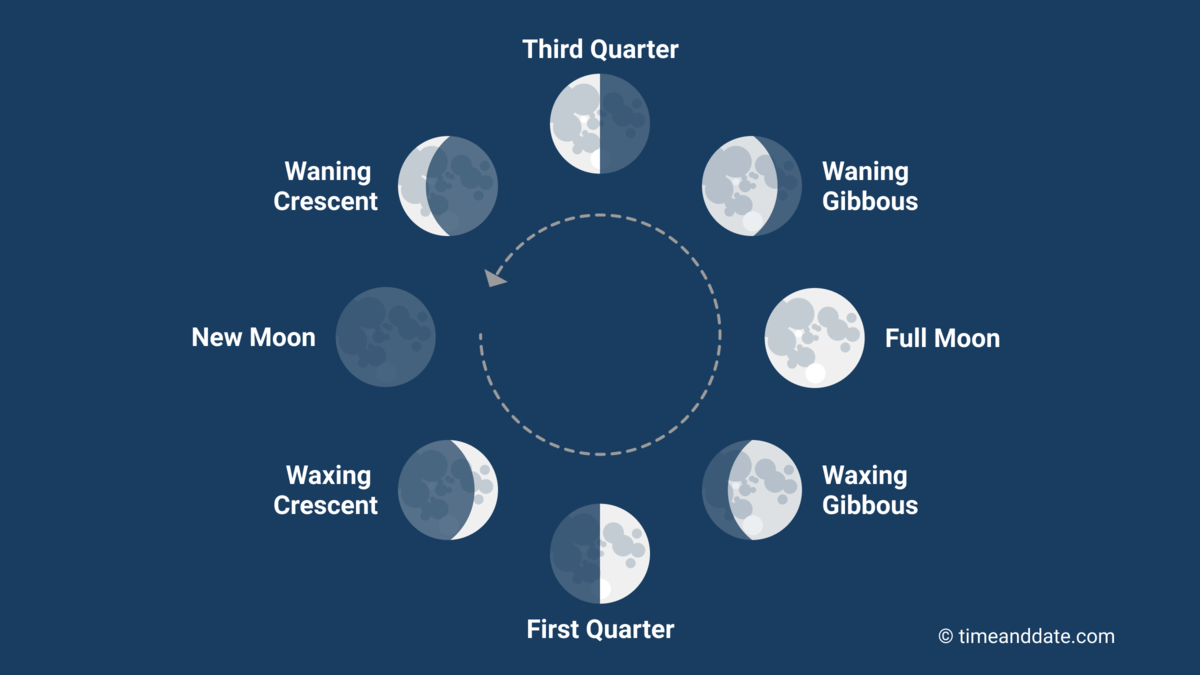
It takes around 29.5 days to move through the eight Moon phases.
©timeanddate.com
Opposite Sides in Opposite Hemispheres
At the Third Quarter in the Northern Hemisphere, the lit up half of the Moon appears on the left, while in the Southern Hemisphere it appears on the right. Near the equator, the Moon is oriented so that the lower part is bright after moonrise, and the upper part is bright before moonset.
Is the Moon upside-down in the other hemisphere?
Third Quarter Moon in Calendars
The symbol for Third Quarter Moon in modern calendars is a circle split down the middle with the left side white and the right side black.
The other primary Moon phase symbols in calendars: = New Moon
= First Quarter
= Full Moon
The Moon illustration on our Moon phase pages changes as time passes and indicates more accurately, although not perfectly, the orientation of the illuminated part of the Moon.
Sleep, crime, and menstruation: how Moon phases affect humans
Affects the Tides
The ocean tides on Earth are mostly generated by the Moon’s gravitational pull. At the First and Third Quarter, the Moon and Sun pull in different directions, producing the smallest difference between high and low tide, known as neaps or neap tide.
The largest tidal range is around Full Moon and New Moon. During these Moon phases, the Moon and the Sun’s gravitational forces combine to pull the ocean’s water in the same direction. These tides are known as spring tides or king tides.